[成果] 最少观测节点数精确定位复杂网络中的传播源头
研究成果:Hu Z L, Han X, Lai Y C, Wang W X. Optimal Localization of Diffusion Sources in Complex Networks, Royal Society Open Science, 2017, 4(2): 170091. (DOI: 10.1098/rsos.170091)
简介:扩散是一个非常普遍的现象,然而,很多扩散过程却给我们带来了巨大的损失,如疾病传播和谣言扩散等。因此,找出这些传播源头对于我们控制或抑制这些有害的扩散具有非常重要的意义。关于复杂网络中的传播源头定位,目前的研究方法主要包括极大似然估计、BP 方法及反向传播推断。基于这些方法的研究工作都有各自的优缺点,有的研究工作只需知道某个时刻部分观测节点的信息便能较准确地推断出传播源头,有的研究工作对于初始传播时刻未知时也有效。但是他们存在两个问题:第一,当传播源头较多时效果比较差,甚至根本不可行;第二,所用的观测节点比例较高。那么给予网络结构,对于线性时不变扩散系统,当初始传播时刻未知时,是否存在最少的观测节点精确定位任意未知数量的传播源头?
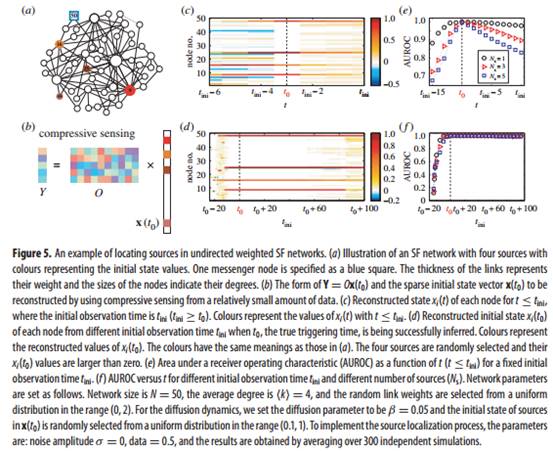
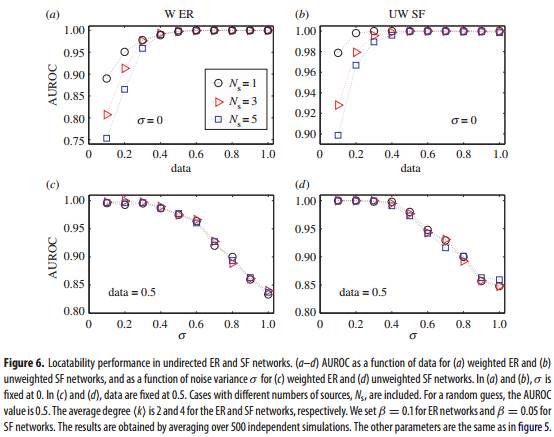
我们将源头定位问题转化为系统初始状态重构问题,如果我们能重构出系统的初始状态,那么就可以精确地定位传播源头。结合严格可控理论,可控与可观之间的对偶关系及PBH定理,我们找出网络完全可观最少需要的观测节点集。最后利用压缩感知方法定位传播源头。我们首先分析了模型网络及大量的实证网络的源头可定位性(网络完全可观最少需要的观测节点比例),发现当网络比较稠密时,源头可定位性越强。对于无向随机权网络,最少观测节点数为孤立子团数。最后我们在模型网络上定位传播源头,发现我们的方法不仅能精确地定位任意数量的传播源头,而且能推出初始传播时刻,同时该方法具有很强的抗噪性。
Abstract: Locating sources of diffusion and spreading from minimum data is a significant problem in network science with great applied values to the society. However, a general theoretical framework dealing with optimal source localization is lacking. Combining the controllability theory for complex networks and compressive sensing, we develop a framework with high efficiency and robustness for optimal source localization in arbitrary weighted networks with arbitrary distribution of sources. We offer a minimum output analysis to quantify the source locatability through a minimal number of messenger nodes that produce sufficient measurement for fully locating the sources. When the minimum messenger nodes are discerned, the problem of optimal source localization becomes one of sparse signal reconstruction, which can be solved using compressive sensing. Application of our framework to model and empirical networks demonstrates that sources in homogeneous and denser networks are more readily to be located. A surprising finding is that, for a connected undirected network with random link weights and weak noise, a single messenger node is sufficient for locating any number of sources. The framework deepens our understanding of the network source localization problem and offers efficient tools with broad applications.
论文链接:http://rsos.royalsocietypublishing.org/content/4/4/170091