相对流动性与取样时间间隔 HighlightsAbstract
我们基于中国健康和营养调查的中国家庭收入数据和货币转移模型,分别从实证和理论两个方面研究了相对流动性与取样时间间隔的关系。实证结果表明,相对流动性随着取样时间间隔变长逐渐增加直至达到一个稳定值。我们利用货币转移模型展示二者之间的关系,得到了与实证结果相近的特性。
研究成果:
The time-dependent characteristics of relative mobility
Highlights
- •
-
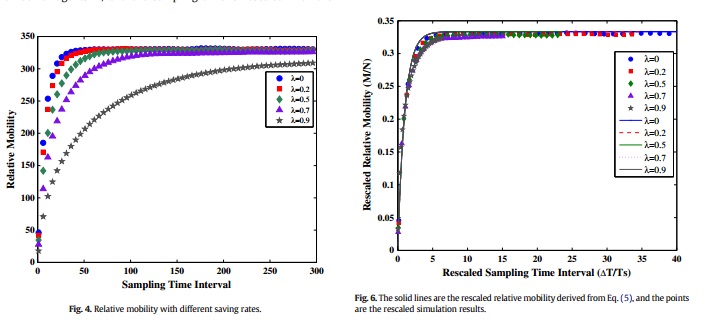
We examine the relation between the relative mobility and the sampling time interval.
- •
-
The empirical finding in household income is reproduced by a money exchange model.
- •
-
A characteristic time interval can specify the convergence rate of the relative mobility.
Abstract
Mobility is a significant supplementary piece of information when discussing the inequality of a society based on income distribution. To date, most of its characteristics require disambiguation and specification. In this paper, we will investigate the dependence of relative mobility on sampling time interval both empirically and theoretically. Using the Chinese household income data from the China Health and Nutrition Survey, we find that the relative mobility will initially increase with the sampling time interval and then approach a constant value. To examine this time-dependent characteristic of mobility quantitatively, we employ a money exchange model with uniform saving rate to investigate the relation between the mobility and the sampling time interval. The relation obtained from the model is similar to that of the empirical data. The convergence rate of the mobility can be described in terms of a characteristic time interval found to be solely determined by the saving rate. The higher the saving rate is, the longer the characteristic time interval is. This work can help us better understand the time-dependence of mobility.
原文链接:
/ckfinder/userfiles/files/1-s2_0-S0264999313005166-main.pdf



