[成果] 生物能源在能源、食物和自然生态系统可持续中的地位
研究成果:Lilibeth A., D. Magcale-Macandog, K. Kumar, X. Cui, E. Eugenio, P. Macandog, A. Salvacion, J. Eugenio, 2016: The role of bioenergy in enhancing energy, food and ecosystem sustainability based on societal perceptions and preferences in Asia, Agriculture, 6, 2, 19.
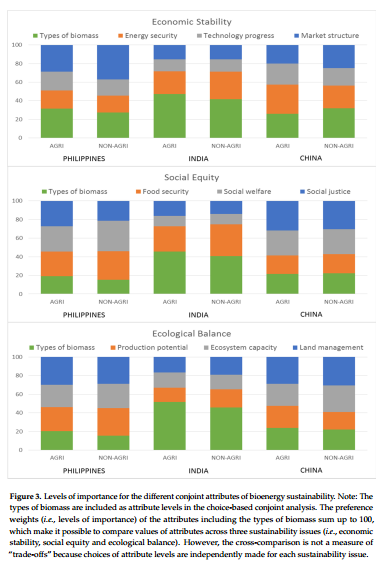
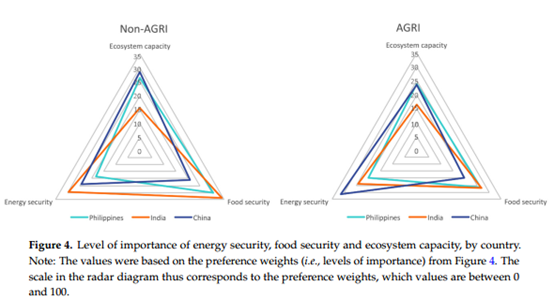
简介:文章讨论了关于菲律宾、印度和中国生物能源可持续性的调查分析。调查问题主要包括:(a)对于生物能源的认识程度;(b)职业和生物能源的关系;(c)对于多种经济原料和生物能源对食品安全影响的看法。另外,还收集了基于生物能源对社会稳定性、社会福利和生态平衡的共同选择等的偏好权重,用以体现能源安全、食品安全和生态系统对其他经济结构的包容性、社会和环境宗旨的重要性。收集的基本观点包括:第一代原料目前正在各个国家被用作生物燃料的生产,并且这些被认为对经济有着很重要的作用。在这个研究成果的基础上,对于生物能源这个角色的偏爱反映了这些国家的社会和经济关注点(中国的能源安全、印度的食品安全和菲律宾的生态系统退化)。
Abstract
This paper discussed the analysis of the survey on sustainability of bioenergy conducted
in the Philippines, India and China. It acquired general perceptions of the people by asking them (a) specific questions about their level of familiarity with bioenergy; (b) relationship of their work to bioenergy; and (c) their opinion on contribution of various feedstock on the economy and impact of bioenergy production on food security. In addition to these questions, we estimated preference weights of various feedstock based on the conjoint choices on bioenergy’s contribution to social stability, social welfare and ecological balance. The estimates revealed significant trade-offs not only among these three dimensions of sustainability but also the relative importance of energy security, food security and ecosystem capacity to other economic, social and environmental objectives. The types of first generation feedstock that are currently used for biofuel production in the respective countries and those that offer alternative household use are perceived as important to the economy and preferred bioenergy feedstock. Based on the results of the study, the preferred role of bioenergy for sustainable development reflects the social and economic concerns in the respective Asian countries, e.g., energy security in China, food security in India, and ecosystem degradation in the Philippines.