[成果] 复杂网络中的连边级联失效
研究成果:Y. Feng, B. Sun, A. Zeng*, Cascade of links in complex networks, Phys, Lett. A(2017), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2016.11.008
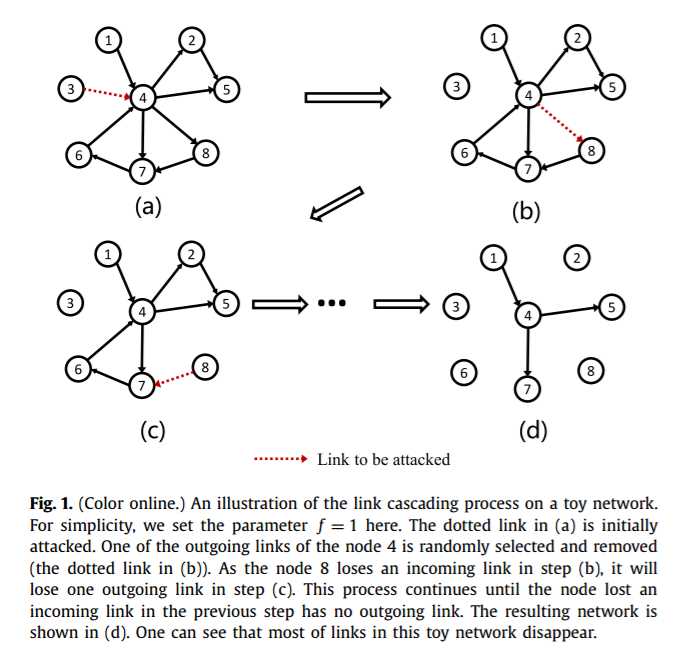
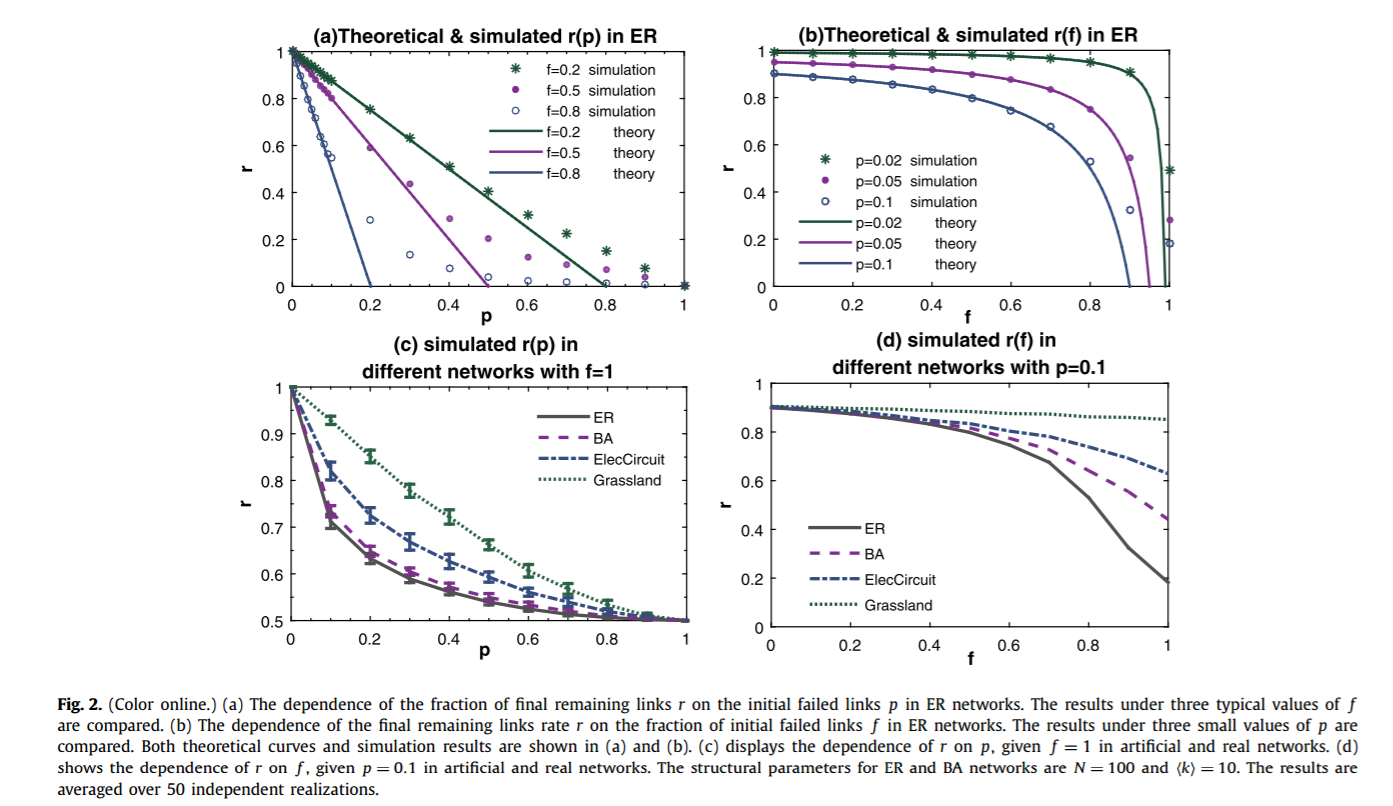
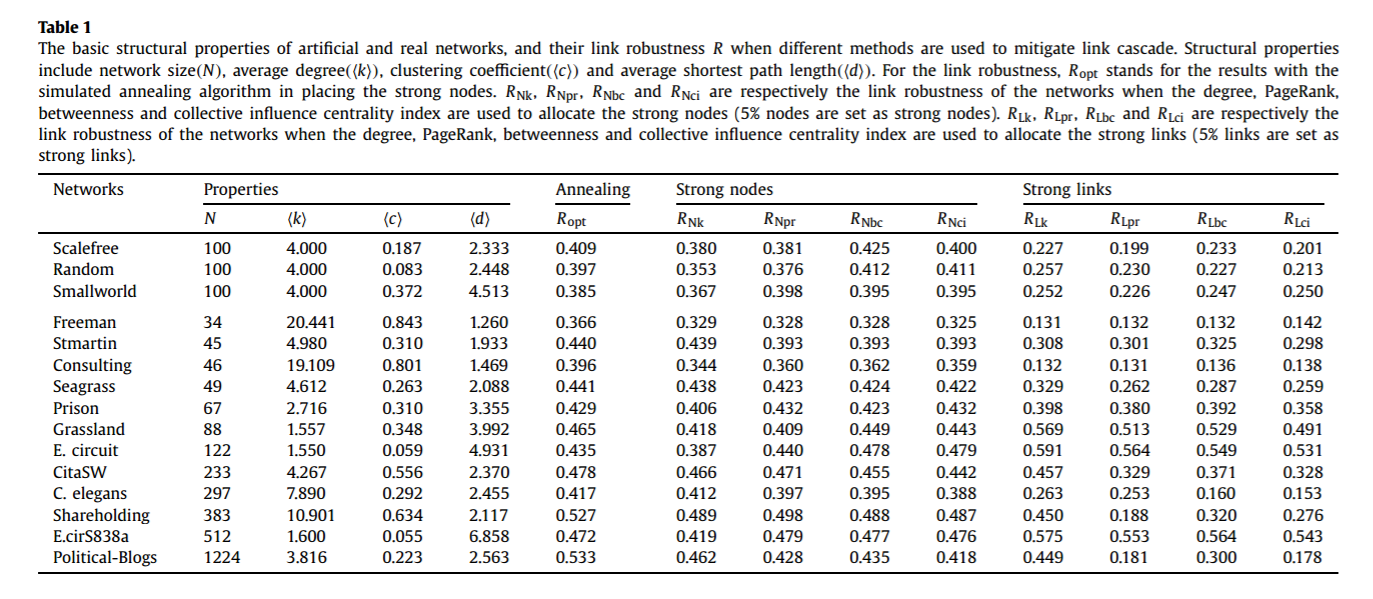
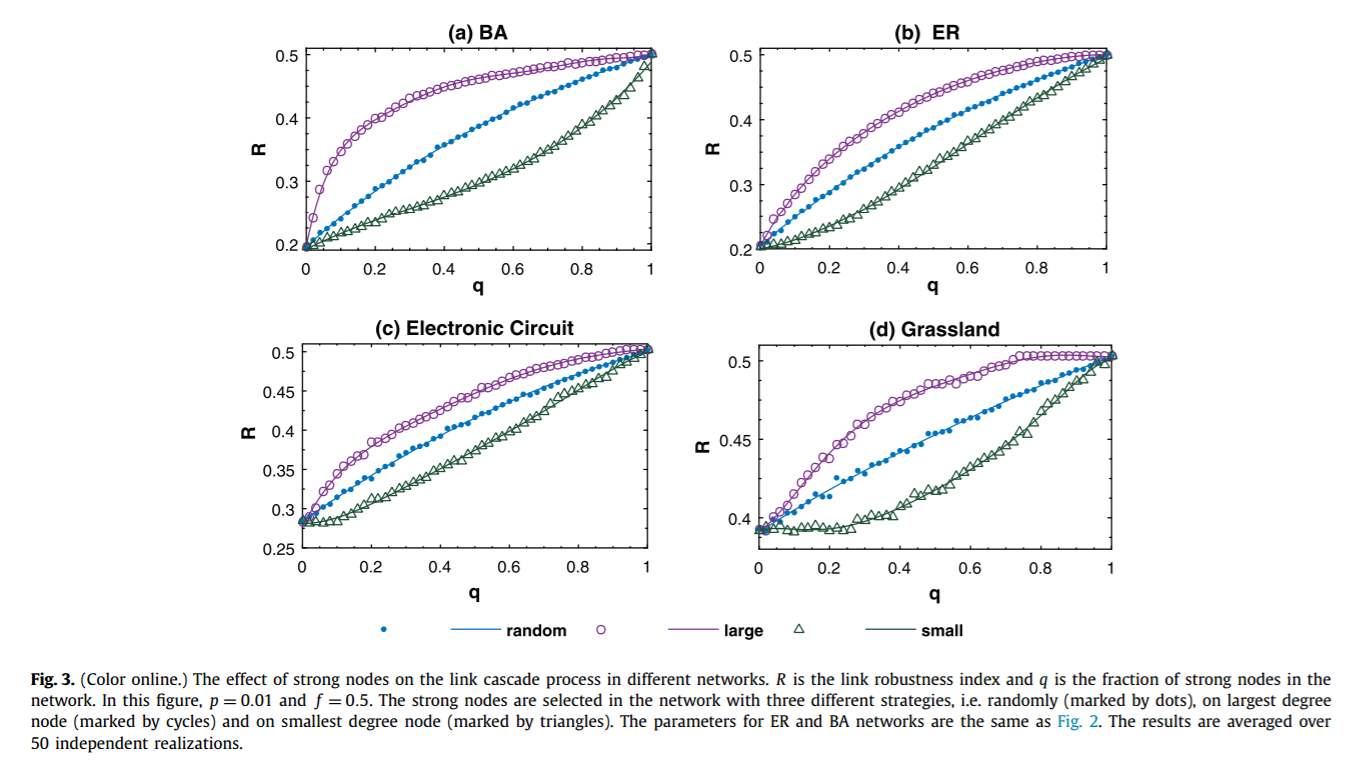
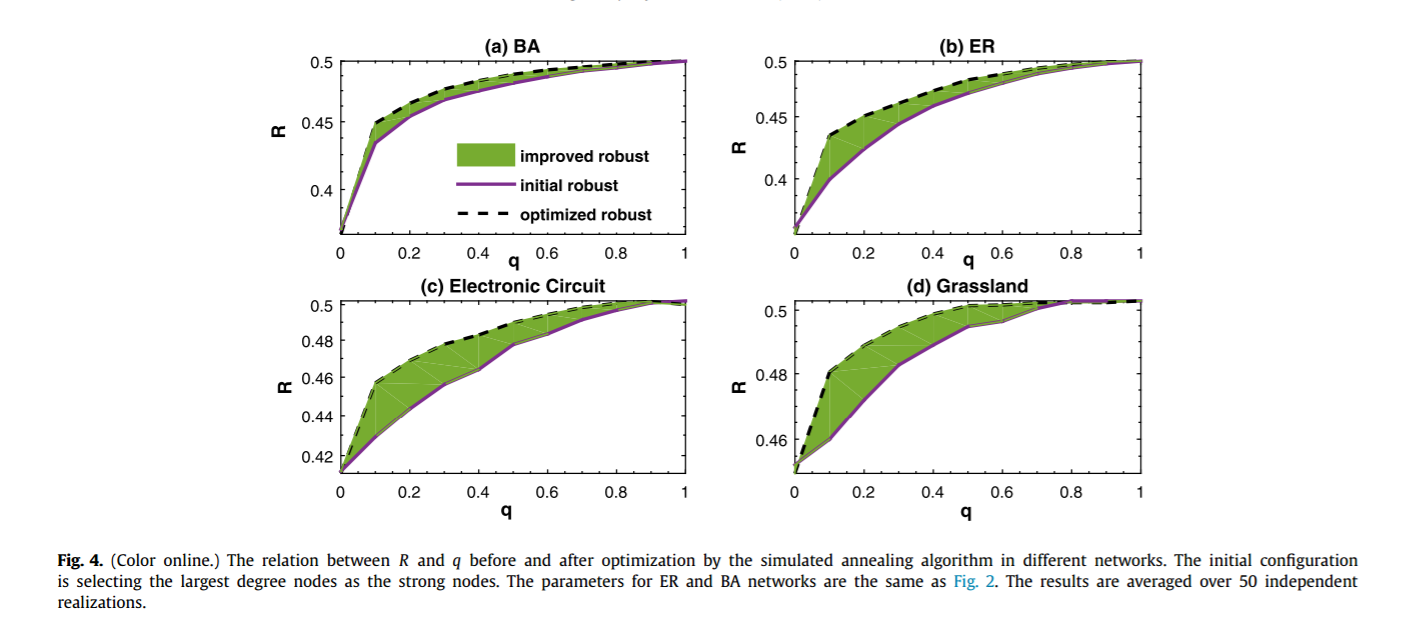
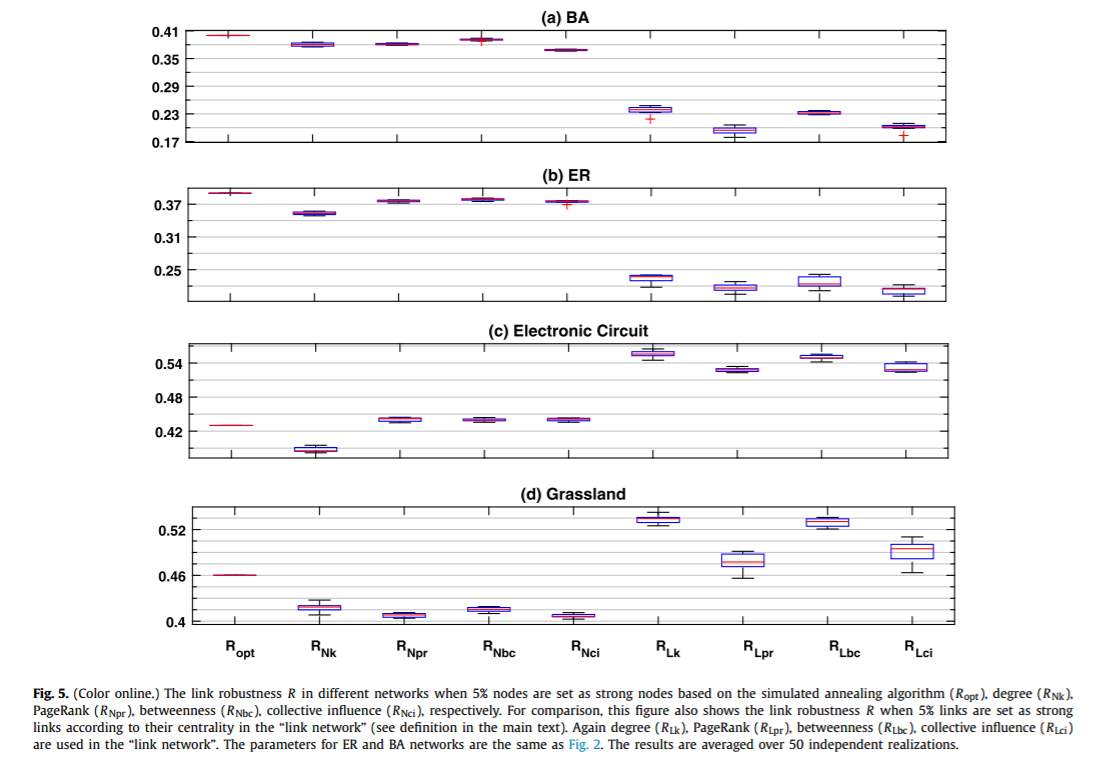
简介:在复杂网络的研究中,级联失效被广泛用于建模灾难性时间,例如实际系统中的航班延误与金融危机等。但是,目前关于级联失效的研究大多集中于节点上而忽视了连边。实际情况中,由于连边受到攻击而触发的级联失效会更加普遍。例如在金融系统中,金融机构(节点)不容易消失,但是他们之间的贸易关系(连边)发生断裂却很容易触发级联失效;航空系统中也有类似的情况。通过这个连边级联失效的模型,我们发现模型网络与实际网络都会由于少量连边的损失触发全局性的级联失效,而这个过程可以通过人工设置少量可以阻断风险传播的节点或连边(这类节点或者连边无法将风险继续传递下去)来得到有效的抑制。最后,我们通过使用模拟退火算法,可以针对每一个特殊的网络设计出最优的可以阻断风险的节点、连边组合方式,进而在提高实际系统的鲁棒性中有重要的意义。
Abstract:
Cascading failure is an important process which has been widely used to model catastrophic events such as blackouts and financial crisis in real systems. However, so far most of the studies in the literature focus on the cascading process on nodes, leaving the possibility of link cascade overlooked. In many real cases, the catastrophic events are actually formed by the successive disappearance of links. Examples exist in the financial systems where the firms and banks (i.e. nodes) still exist but many financial trades (i.e. links) are gone during the crisis, and the air transportation systems where the airports (i.e. nodes) are still functional but many airlines (i.e. links) stop operating during bad weather. In this letter, we develop a link cascade model in complex networks. With this model, we find that both artificial and real networks tend to collapse even if a few links are initially attacked. However, the link cascading process can be effectively terminated by setting a few strong nodes in the network which do not respond to any link reduction. Finally, a simulated annealing algorithm is used to optimize the location of these strong nodes, which significantly improves the robustness of the networks against the link cascade.
原文链接:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2016.11.008