[成果] 气候变化对于蒙古高原植被的畜牧业的影响研究
研究成果:Miao, L., R. Fraser, Z. Sun, D. Sneath, B. He,and X. Cui*, 2016: Climate impact on vegetation and animal husbandry on the Mongolian plateau: a comparative analysis. Natural Hazards, 80(2),727-739.
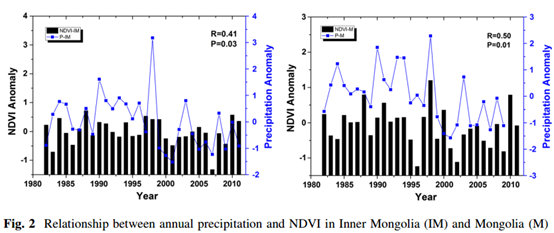
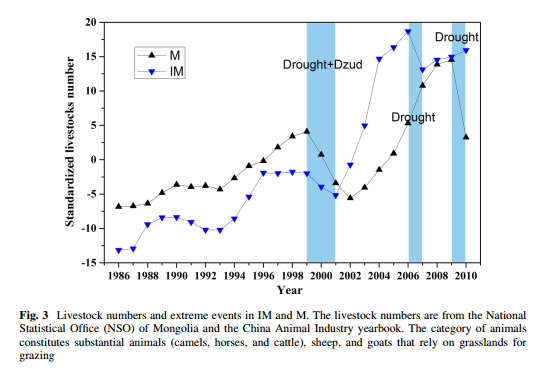
简介:目前干旱半干旱区是国际研究热点区域,因为气候变化对这些地区的的植被和畜牧业等早已经产生了巨大的影响。本文基于气象学数据、GIMMS AVHRR NDVI3g数据和牲畜记录,通过统计学分析,了解到在这些区域正发生着强烈的变暖和降水量的下降。降水模式正在改变,并且频率越来越高的极端气候,比如干旱等,都是危害到植被生长和畜牧业发展的主要原因。通过对比分析,我们探索了内蒙和外蒙这两个区域的植被和畜牧业分别对气候变化和极端气候的响应。我们发现,植被生长大体从十九世纪中期开始下降,然后从2001年起又开始恢复。内蒙的农业集约化水平比外蒙高,并且内蒙的居民比外蒙的居民对气候变化有更加强烈的感觉。为了解决这些问题,我们呼吁未来更多关注着这个地区的极端气候研究。
Abstract
International research has focused more attention on arid and semiarid regions in recent years, as climate change has already had adverse impacts on grasslands and local households in the Mongolian plateau. Based on meteorological data, GIMMS AVHRR NDVI3g data, and livestock records, through statistical analysis, a significantly strong warming trend and a slightly decreasing trend in precipitation were ascertained in this region. Precipitation patterns are shifting, and intensifying, extreme events, such as droughts and dzud (extremely harsh winters characterized by heavy snow and low temperature), are a major threat to vegetation growth and animal husbandry development. Following a comparative analysis approach, we explored how the vegetation and animal husbandry response to climate change and extreme weather differ between Inner Mongolia and Mongolia. We found that vegetation growth generally decreased after the mid-1990s, but began to recover from 2001 over the entire region. The agricultural intensification level is higher in Inner Mongolia than in Mongolia, and residents in Inner Mongolia have a greater awareness of unexpected disasters than those in Mongolia. To deal with these challenges, this region warrants further study on how climate extremes will impact on regional animal husbandry and local social economics on the arid and semiarid regions. This could have implications for the international community, local government, local residents, and future scientific activities in this space.
原文链接:http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11069-015-1992-3