[成果] 复杂网络上的目标传播
研究成果: Sun, Y., Ma, L., Zeng, A., Wang, W. X. (2016). Spreading to localized targets in complex networks. Sci. Rep. 6, 38865; doi:10.1038/srep38865 (2016).
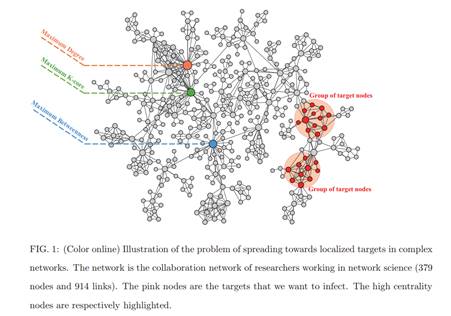
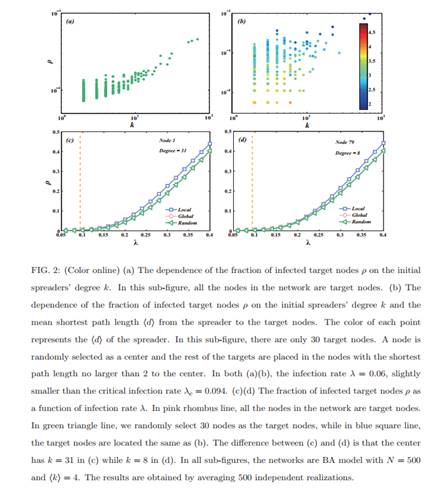
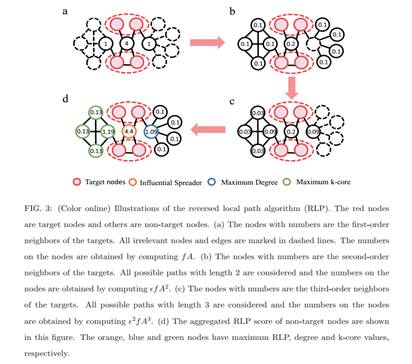
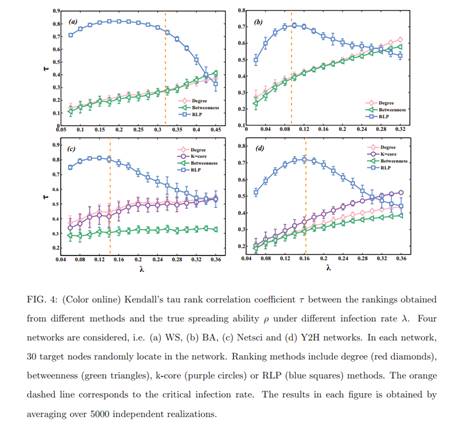
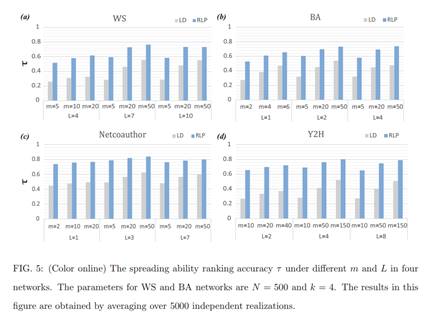
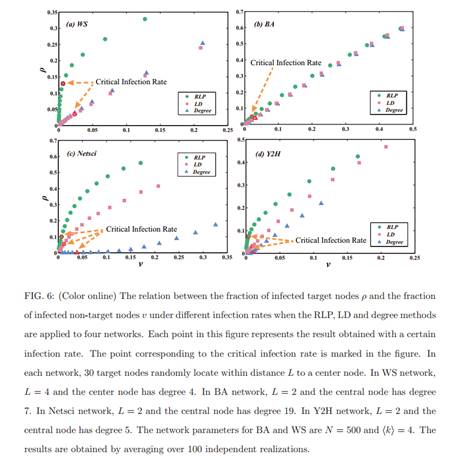
简介:传播作为一种重要的动力学被广泛地用于模拟许多真实的过程,例如流行病和信息的传播。其中一个最重要的研究问题就是为节点的传播能力排序。为了这个目的,已经有一系列有效的方法被提出。这些方法通常定义node i的传播能力为在给定最初传播源node i的情况下,它最终感染的网络中节点的数量。但是,在很多真实的情况下,例如广告和新闻传播,我们的目标仅仅是感染网络中一部分的目标节点。因此,非常有必要去研究对那些局域的目标节点的节点传播能力。在这篇文章中,我们提出了一种逆向局域路径的方法(RLP)来解决这一问题。仿真结果显示,我们的方法在识别那些对于局域的目标节点有影响力的节点方面比现有的方法好。除此之外,被我们的方法所识别的有影响力的节点还可以在传播过程中有效地避免感染那些非目标节点。
Abstract:
As an important type of dynamics on complex networks, spreading is widely used to model many real processes such as the epidemic contagion and information propagation. One of the most significant research questions in spreading is to rank the spreading ability of nodes in the network. To this end, substantial effort has been made and a variety of effective methods have been proposed. These methods usually define the spreading ability of a node as the number of finally infected nodes given that the spreading is initialized from the node. However, in many real cases such as advertising and news propagation the spreading only aims to cover a specific group of nodes. Therefore, it is necessary to study the spreading ability of nodes towards localized targets in complex networks. In this paper, we propose a reversed local path algorithm for this problem. Simulation results show that our method outperforms the existing methods in identifying the influential nodes with respect to these localized targets. Moreover, the influential spreaders identified by our method can effectively avoid infecting the non-target nodes in the spreading process.
原文链接:www.nature.com/articles/srep38865